Introduction
Oral health plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. Tooth problems can arise due to various reasons, and one common issue is a dead tooth. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for a dead tooth.
What is a Dead Tooth?
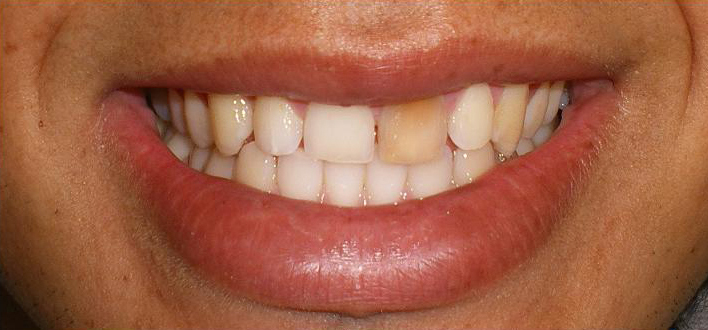
A dead tooth, also known as a non-vital tooth, is a tooth that no longer receives a blood supply. It occurs when the pulp inside the tooth, which contains nerves and blood vessels, becomes infected or damaged. Without proper treatment, a dead tooth can lead to complications and further oral health problems.
Causes of Dead Tooth
There are several factors that can contribute to the death of a tooth. Some common causes include:
- Trauma: A strong impact or injury to the tooth can damage the blood vessels and nerves, leading to tooth death.
- Tooth Decay: Untreated tooth decay can progress and reach the inner layers of the tooth, causing infection and eventual tooth death.
- Dental Procedures: Certain dental procedures, such as root canals or fillings, can occasionally result in a dead tooth if complications arise.
- Gum Disease: Advanced gum disease can cause the supporting structures of the tooth to deteriorate, leading to tooth death.
Symptoms of a Dead Tooth
Identifying a dead tooth can be challenging as it may not always cause noticeable symptoms. However, some common signs to watch out for include:
- Discoloration: A dead tooth often turns gray, black, or dark yellow compared to the surrounding teeth.
- Toothache: Intermittent or persistent tooth pain, especially when biting or chewing, can indicate a dead tooth.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures in a specific tooth may be a sign of tooth death.
- Swelling and Abscess: In some cases, a dead tooth can lead to a pimple-like swelling on the gum, accompanied by pain and discharge.
Diagnosing a Dead Tooth
If you suspect a dead tooth, it is essential to visit a dentist for a proper diagnosis. The dentist will perform a thorough examination, including:
- Visual Inspection: The dentist will examine the tooth for discoloration, cracks, or other visible signs of damage.
- X-rays: X-ray images can reveal the condition of the tooth’s roots, surrounding bone, and any signs of infection.
- Pulp Vitality Test: A pulp vitality test involves applying a cold stimulus to check the tooth’s response. A lack of response may indicate a dead tooth.
Treatment Options for a Dead Tooth
The treatment for a dead tooth depends on various factors, including the extent of damage and the patient’s overall oral health. Here are the three main treatment options:
- Root Canal Therapy: This is the most common treatment for a dead tooth. It involves removing the infected or damaged pulp, cleaning the root canals, and filling them with a dental material. Afterward, a crown is placed over the tooth to protect and restore its function.
- Dental Extraction: If a dead tooth cannot be saved or if it poses a risk to the surrounding teeth and tissues, extraction may be necessary. After extraction, options like dental implants or bridges can be considered to fill the gap.
- Dental Implant: A dental implant is an artificial tooth root that is surgically placed into the jawbone. It provides a stable foundation for a replacement tooth, which is then attached to the implant. Dental implants are a long-lasting solution for replacing a dead tooth.
Prevention of Dead Tooth
Preventing a dead tooth involves maintaining good oral hygiene and taking precautionary measures. Here are some preventive tips:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and floss daily.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings.
- Wear a mouthguard during sports activities to protect your teeth from injuries.
- Treat tooth decay promptly to prevent infection from reaching the inner layers of the tooth.
- Practice good oral hygiene habits, including a balanced diet and limiting sugary foods and drinks.
Summary
A dead tooth can have a significant impact on your oral health and overall well-being. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely treatment are crucial to preserving your natural teeth. Remember to maintain good oral hygiene practices and visit your dentist regularly to prevent tooth problems. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a healthy and vibrant smile for years to come.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can a dead tooth be saved without a root canal?
In some cases, if the tooth is not severely damaged, alternative treatments like pulp capping or revascularization may be possible. However, a root canal is often the preferred treatment to save a dead tooth.
2. Is a dead tooth painful?
A dead tooth may not always cause pain. However, if an infection develops, it can lead to discomfort, swelling, and pain.
3. How long does a root canal treatment take?
The duration of a root canal treatment depends on the complexity of the case. It can range from one to three visits to complete the procedure.
4. Can a dead tooth affect neighboring teeth?
Yes, if a dead tooth is left untreated, the infection can spread to the surrounding teeth, gums, and bone, potentially causing further oral health issues.
5. Can a dead front tooth be replaced with a dental implant?
Yes, a dental implant can be used to replace a dead front tooth. It provides a natural-looking and functional solution to restore your smile.
You can also read about this please visit:StrongHealthy.us