Introduction
In the realm of real estate investing, navigating the complex landscape of taxes can be a daunting task. However, one tool that has gained prominence for its ability to simplify tax obligations while maximizing returns is the Section 1031 Exchange. This article aims to provide an in-depth review of “Section 1031 Exchange: Tax-Deferred Investing Made Simple,” shedding light on the intricacies of this powerful investment strategy.
Understanding Section 1031 Exchanges
Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code allows investors to defer capital gains tax when they exchange one investment property for another of like-kind. This tax-deferral mechanism is a game-changer for investors seeking to optimize their wealth accumulation strategies.
Importance of Tax-Deferred Investing
Tax considerations can significantly impact the profitability of real estate investments. By utilizing Section 1031 exchanges, investors can strategically manage their tax liability, enabling them to reinvest more capital into new properties. This, in turn, accelerates wealth accumulation and portfolio growth.
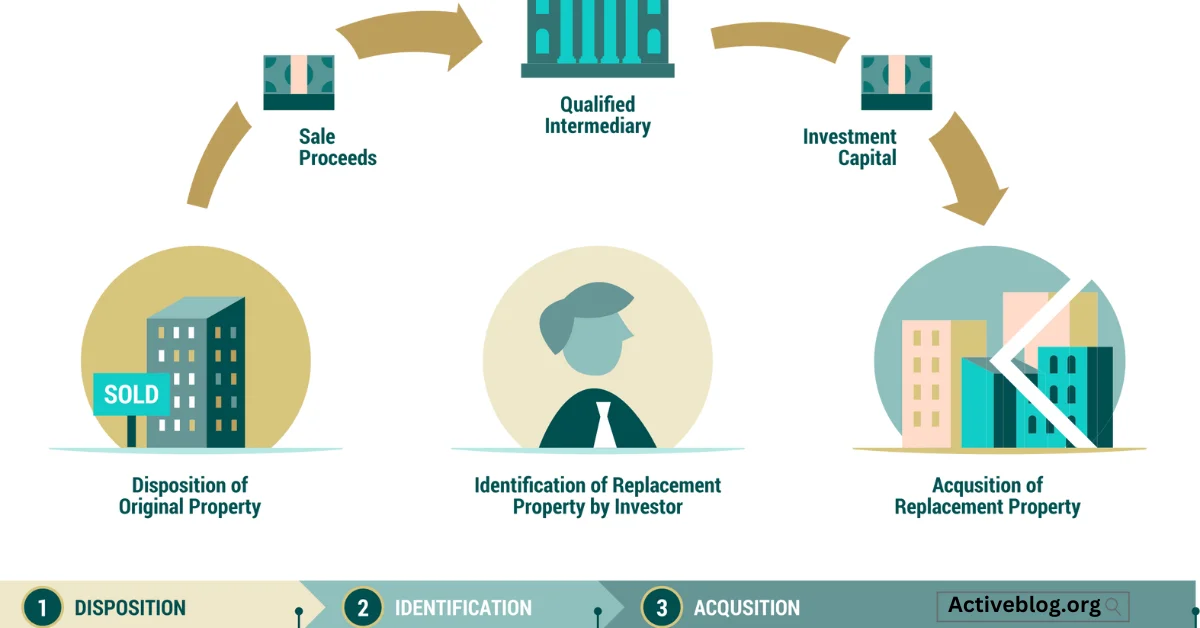
How Section 1031 Exchanges Work
Basic Principles
Section 1031 exchanges are based on a few fundamental principles. Firstly, the properties involved must be of like-kind, which is a broad term encompassing various types of real estate. Secondly, the exchange should be properly structured to comply with IRS regulations. Finally, the investor must adhere to strict timelines and deadlines throughout the exchange process.
Types of Properties Eligible for Exchange
One of the appealing aspects of Section 1031 exchanges is the wide range of eligible properties, including residential, commercial, and even vacant land. This flexibility allows investors to diversify their portfolios seamlessly.
Timelines and Deadlines
Navigating the exchange process requires meticulous attention to deadlines. Investors have 45 days to identify potential replacement properties and 180 days to complete the exchange successfully. These timelines are non-negotiable, making it crucial to plan ahead.
Benefits of Section 1031 Exchanges
Tax Savings
The primary benefit of a Section 1031 exchange is the deferral of capital gains tax. By deferring tax payments, investors can reinvest the full proceeds from the sale into a new property, increasing the potential for growth and income generation.
Portfolio Diversification
Diversifying one’s real estate portfolio is essential for mitigating risks. Section 1031 exchanges facilitate this diversification by allowing investors to switch from one type of property to another without incurring immediate tax consequences.
Wealth Accumulation
Over time, the tax savings generated by Section 1031 exchanges can accumulate significantly. This can lead to substantial wealth accumulation, positioning investors for long-term financial success.
Step-by-Step Guide to a Section 1031 Exchange
Identifying Replacement Property
The process begins with identifying suitable replacement properties within 45 days of the sale of the relinquished property. Careful consideration must be given to property types, location, and value.
Initiating the Exchange
To ensure a successful exchange, it’s advisable to engage a qualified intermediary (QI). They play a crucial role in facilitating the exchange and ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
Completing the Exchange
The exchange is completed within 180 days of the initial sale. The investor acquires the replacement property, and the QI facilitates the transfer of funds from the sale of the relinquished property to the purchase of the new one.
Common Misconceptions
Exchanging Primary Residences
One common misconception is that Section 1031 exchanges can be used for primary residences. In reality, these exchanges are exclusively for investment properties.
The Role of Intermediaries
Some investors question the necessity of intermediaries in the exchange process. Intermediaries are essential to ensure that the exchange meets IRS requirements and that the tax deferral remains intact.
New Tax Basis for Replacement Property
It’s crucial to understand that while capital gains tax is deferred in a Section 1031 exchange, it is not eliminated entirely. When the replacement property is eventually sold, the deferred tax liability may come due unless further exchanges are executed.
Real-Life Examples
Case Study 1: Commercial Real Estate
Let’s delve into a real-life example. Imagine you own a commercial property valued at $1 million and decide to exchange it for another commercial property of equal value. By utilizing a Section 1031 exchange, you defer capital gains tax and maintain the full $1 million for reinvestment.
Case Study 2: Residential Property
Suppose you own a residential rental property worth $500,000. Through a Section 1031 exchange, you can swap it for another income-generating residential property. This not only defers taxes but also allows you to diversify your rental property portfolio.
Risks and Considerations
Market Fluctuations
While Section 1031 exchanges offer tax benefits, they do not shield investors from market fluctuations. It’s crucial to carefully evaluate the potential risks associated with the replacement property.
Non-Qualified Exchanges
Non-compliance with IRS regulations can result in the disqualification of the exchange, leading to immediate tax liability. Due diligence and professional guidance are essential to avoid this pitfall.
Exit Strategies
Investors should also consider their long-term exit strategies. Section 1031 exchanges can be used multiple times, but eventually, taxes may become due. It’s important to plan for these eventualities.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Investment Journey
In conclusion, Section 1031 exchanges are a powerful tool for tax-deferred investing that can simplify the real estate investment landscape. By understanding the fundamental principles, benefits, and intricacies of this strategy, investors can take control of their financial future and accelerate their path to wealth accumulation.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can I use a Section 1031 exchange for my primary residence?
- No, Section 1031 exchanges are exclusively for investment properties.
2. Are there limitations on the types of replacement properties I can choose?
- Replacement properties must be of like-kind, but there is flexibility within this definition.
3. What is the role of a qualified intermediary in a Section 1031 exchange?
- A qualified intermediary facilitates the exchange process and ensures compliance with IRS regulations.
4. Can I use a Section 1031 exchange tax-deferred multiple times?
- Yes, you can use Section 1031 exchanges repeatedly, but eventual tax liability may accrue.
5. How do market fluctuations affect Section 1031 exchanges?
- Market fluctuations can impact the value and performance of replacement properties, so careful evaluation is essential.
By harnessing the power of Section 1031 exchanges and understanding its nuances, investors can embark on a journey towards financial empowerment tax-deferred and tax-efficient wealth accumulation. Start exploring this strategy to unleash the full potential of your real estate investments.